
Products
Uracil Powder China 2-Amino-5-chlorobenzophenone Manufacture Supplier – Longo Detail:
Structural Formula
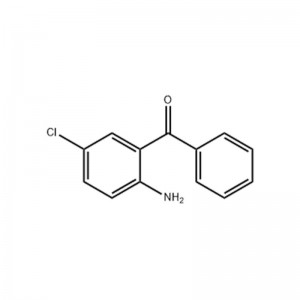
Physical
Appearance: Yellow crystalline powder
Density: 1.33
Melting point: 96-98 °C (lit.)
Boiling point: 207 °C
Refractivity: 1.6000 (estimate)
Flash point: 211 °C
Safety Data
General
Application
A metabolite of Diazepam; it had a much weaker anticonvulsant effect.
Pharmaceutical intermediates. Manufacture of drugs such as Librium and Valium.
Environmental impact
Slightly hazardous to water, do not allow undiluted or large quantities to come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems, and do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission
Properties and Stability
Stable at ambient temperature and pressure, avoid contact with oxides
Storage methods
Keep container tightly closed and store in a cool, dry place in a tightly packed container.
Synthesis method
(1) Produced by the reaction of p-chloroaniline with benzoyl chloride. Add p-chlorobenzene to the glass-lined reaction pot at 70°C or below, put in anhydrous zinc chloride, add benzoyl chloride dropwise with stirring, then raise the temperature, hold at 195-205°C for 2h, wash five times with hot water at 90-95°C (the water layer and the washing solution recover benzoic acid and zinc chloride) at about 100°C, add sulfuric acid slowly, hold at 142°C for 40min. The solids are precipitated in water. Under stirring, the pH is adjusted with liquid alkali to no higher than 1 and filtered at 20-25 °C. The filtrate is recovered as p-chloroaniline. The filter cake is mixed and suspended in water, neutralised to pH=6, filtered dry, washed with water to neutral and dried to obtain the crude product. Then add 6-7 times ethanol, 6% activated carbon, reflux for 30min, filter and crystallize, dry to obtain the fine product. (2) p-Nitrochlorobenzene and cyanobenzyl ring combination to obtain isoxazole, then open the ring, the reduction to obtain.
Product detail pictures:
Related Product Guide:
Each individual member from our large performance revenue crew values customers' needs and company communication for Uracil Powder China 2-Amino-5-chlorobenzophenone Manufacture Supplier – Longo , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Guinea, Macedonia, Mali, As the world economic integration bringing challenges and opportunities to the xxx industry, our company , by carrying on our teamwork, quality first, innovation and mutual benefit, are confident enough to provide our clients sincerely with qualified products, competitive price and great service, and to build a brighter future under the spirit of higher, faster, stronger with our friends together by carrying on our discipline.
This company has a lot of ready-made options to choose and also could custom new program according to our demand, which is very nice to meet our needs.




