Products
Fluorouracil Ointment China Retinoic Acid Manufacture Supplier – Longo Detail:
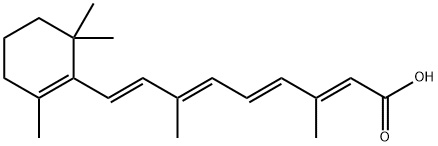
Structural Formula
Physical
Appearance:Light orange or yellow crystalline powder
Density:1.0597 (rough estimate)
Melting point:180-181 °C (lit.)
Boiling point:381.66°C (rough estimate)
Refractivity:1.4800 (estimate)
Safety Data
general
Application
Retinoic acid (tretinoin) is a vitamin A derivative. It has demonstrated an ability to alter collagen synthesis, increase dermal hyaluronic acid levels, and stimulate fibroblast growth and the extracellular matrix. It is used for keratinization disorders and for treating acne.
Vitamin A, with the molecular formula C20H28O2, is a metabolic intermediate product of vitamin A in the body, mainly affecting bone growth and promoting the metabolic effects of epithelial cell proliferation, differentiation and keratinolysis. It is used for the treatment of acne vulgaris, psoriasis, ichthyosis, lichen planus, hair red furunculosis, follicular keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
Category: Anti-skin keratinisation abnormalities, cell inducing differentiation agents
Storage conditions: light-proof and sealed
Retinoic acid has no effect on the tyrosinase activity and melanin composition of normal human melanocytes. When the skin undergoes physiological ageing or is damaged by drugs, UV radiation or trauma, retinoic acid corrects or prevents abnormalities in the biochemical composition and morphological structure of the dermal connective tissue caused by harmful factors. Retinoic acid has no effect on normal skin collagen synthesis. In addition, retinoic acid has an inhibitory activity on leukocyte chemotaxis, thus acting as an anti-inflammatory agent. Retinoic acid has no direct effect on the sebaceous glands and their secretion.
Product detail pictures:
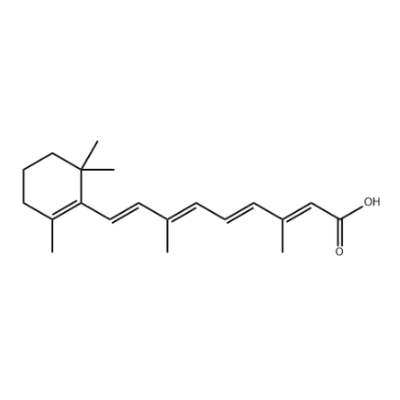
Related Product Guide:
Based on domestic market and expand overseas business is our development strategy for Fluorouracil Ointment China Retinoic Acid Manufacture Supplier – Longo , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Barbados, Ethiopia, Benin, Our company is an international supplier on this kind of merchandise. We supply an amazing selection of high-quality merchandise. Our goal is to delight you with our distinctive collection of mindful items while providing value and excellent service. Our mission is simple: To supply the items and service to our customers at the lowest prices possible.
Product variety is complete, good quality and inexpensive, the delivery is fast and transport is security, very good, we are happy to cooperate with a reputable company!