
Products
Fluorouracil China Triphosgene Manufacture Supplier – Longo Detail:
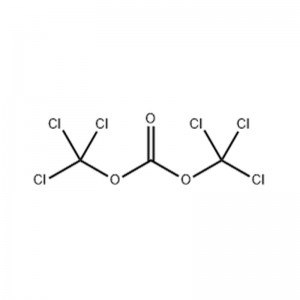
Structural Formula
Physical
Appearance: white granular crystals
Density: 1.78
Melting point: 79-83 °C (lit.)
Boiling point: 203-206 °C (lit.)
Flash point: 203-206 °C (lit.)
Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ether, tetrahydrofuran, benzene, cyclohexane, chloroform and other organic solvents
Safety Data
Hazard category:6.1(8)
Dangerous goods transport no:UN2928
Packaging category:II
Application
It is used to synthesize chloroformates, isocyanates, polycarbonates and acyl chloride.
Triphosgene, also known as di(trichloromethyl)carbonate, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C3Cl6O3, a white crystalline powder that decomposes slightly at the boiling point to produce trichloromethyl chloroformate and phosgene, mainly used in the synthesis of chloroformate, isocyanate, polycarbonate and chloroformyl chloride, etc. It is widely used as an intermediate in plastics, pharmaceuticals, herbicides and pesticides.
It is used in the synthesis of chloroformate, isocyanate, polycarbonate and chloride, etc. Solid phosgene, also known as triphosgene, is synthesized from dimethyl carbonate – a green chemical material, which is highly reactive and can replace phosgene in various chemical reactions, and the main types of reactions it can be involved in are: chloromethylation, carbonic acid esterification, urelation, isocyanate esterification, chlorination, isonitriles, ring formation reactions, alpha-chlorination of aldehydes Formylation, oxidation of alcohols, etc. In organic synthesis, solid phosgene can replace oxalyl chloride as an activator of dimethyl sulfoxide in the oxidation reaction of alcohols and be used conveniently and safely in the preparation of hydroxyl compounds; solid phosgene can also change different types of alcohols into the corresponding chlorinated compounds. In the pharmaceutical industry, solid phosgene can replace phosgene in the synthesis of a large number of pharmaceutical.
Product detail pictures:
Related Product Guide:
Our corporation insists all along the quality policy of product high quality is base of organization survival; purchaser pleasure will be the staring point and ending of an company; persistent improvement is eternal pursuit of staff plus the consistent purpose of reputation very first, purchaser first for Fluorouracil China Triphosgene Manufacture Supplier – Longo , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Liberia, Greek, Bangladesh, Our professional engineering group will always be ready to serve you for consultation and feedback. We are able to also offer you with absolutely free samples to meet your requirements. efforts will likely be produced to give you the ideal service and goods. For anyone who is thinking about our company and merchandise, please contact us by sending us emails or contact us quickly. As a way to know our merchandise and firm. lot more, you can come to our factory to find out it. We'll always welcome guests from all over the world to our business to build company relations with us. Please feel free to get in touch with us for business and we believe we are going to share great trading practical experience with all our merchants.
The factory workers have rich industry knowledge and operational experience, we learned a lot in working with them,we are extremely grateful that we can encount a good company has excellent wokers.






