Products
Chinese wholesale Aztreonam - China Adenosine Manufacture Supplier – Longo Detail:
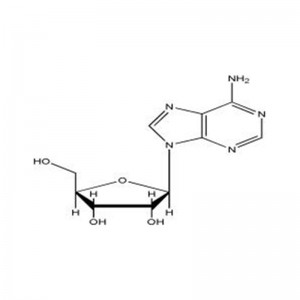
Structural Formula
Physical
Appearance: white crystalline or off-white crystalline powder
Density: 2.08 g/cm³
Melting point: 234 to 236 ℃
Boiling point: 676.3 ℃
refractivity: 1.907
Flash point: 362.8 ℃
Safety Data
Hazardous category.
Dangerous Goods Transport Number.
Packing category.
Application
Adenosine is used to help restore normal heartbeats in people with certain heart rhythm disorders.
Adenosine is also used during a stress test of the heart.
Adenosine may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
Adenosine, a compound consisting of N-9 of adenine linked to C-1 of D-ribose by a β-glycosidic bond, has the chemical formula C10H13N5O4 and its phosphate ester is adenosine acid. Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside that spreads throughout human cells and can directly enter the myocardium to generate adenosine acid by phosphorylation, which is involved in myocardial energy metabolism, as well as in dilating coronary vessels and increasing blood flow. It is used in the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia. Adenosine has physiological effects on the cardiovascular system and many other systems and tissues of the muscle. Adenosine is an important intermediate used in the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenine, adenosine acid, and adenosine asiaticum.
It is also an antiarrhythmic agent that converts paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia to sinus rhythm. It is used for supraventricular arrhythmias related to atrioventricular. Treatment of angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, coronary insufficiency, atherosclerosis, essential hypertension, cerebrovascular disorders, post-stroke sequelae, progressive muscle atrophy, etc. Also used in biochemical studies.
Adenosine is an endogenous purine nucleoside that slows AV node conduction, blocks the AV nodal fold pathway, and restores normal sinus rhythm in patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) (with or without preexcitation syndrome). Adenosine is rapidly taken up by red blood cells and therefore has a short duration of action, with a plasma half-life of less than 10 s. The most common form of PSVT is via the retrograde pathway, so adenosine is effective in terminating this type of arrhythmia. In non-atrial or sinus node regressive arrhythmias (e.g., atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, atrial tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia), adenosine does not terminate them, but can produce temporary atrioventricular or ventricular block, which can help make a differential diagnosis.
Product detail pictures:

Related Product Guide:
We can always satisfy our respected customers with our good quality, good price and good service due to we are more professional and more hard-working and do it in cost-effective way for Chinese wholesale Aztreonam - China Adenosine Manufacture Supplier – Longo , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Jordan, Germany, United States, Our items are widely recognized and trusted by users and can meet continuously changing economic and social needs. We welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business relationships and mutual success!
The company comply with the contract strict, a very reputable manufacturers, worthy a long-term cooperation.