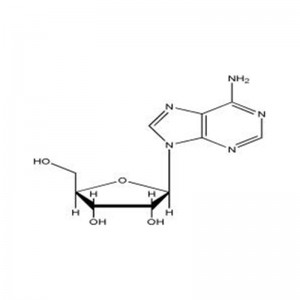
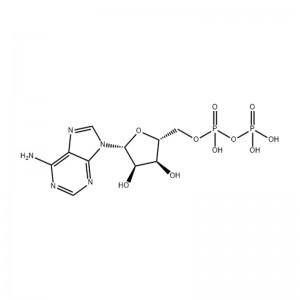
Products
Adenine
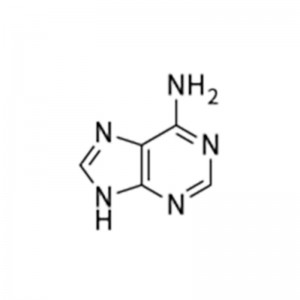
Structural Formula
Physical
Appearance: white crystalline or off-white crystalline powder
Density: 1.6 g/cm³
Melting point: 360-365℃(>360℃(lit.))
Boiling point.
Refractivity.
Flash point: 220 ℃
Safety Data
Hazardous category.
Dangerous Goods Transport Number.
Packing category.
Application
A purine nucleobase and a component of DNA. Widespread throughout animal and plant tissues combined with niacinamide, d-ribose, and phosphoric acids; a constituent of nucleic acids and coenzymes, such as codehydrase I and II, adenylic acid, coa laninedehydrase. It is used in microbial determination of niacin; in research on heredity, virus diseases, and cancer. enteric coating and local antiseptic
Adenine, also known as 6-aminopurine, is one of the four nucleobases that make up DNA and RNA molecules, with the chemical formula C5H5N5. It is involved in the formation of many important intermediates such as ATP and NADP in the metabolic pathways in the body.
Adenine is a component of nucleic acids and coenzymes, involved in the synthesis of DNA and RNA in the body, and is essential for the maintenance of the metabolic functions of the organism. Its role is to promote the proliferation of leukocytes in case of deficiency.
Synthesis
Adenine anabolism includes both ab initio and remedial synthetic pathways. The ab initio synthesis pathway is primarily in the liver and is based on ribose phosphate, aspartate, glycine, glutamine, and one-carbon units. Purine nucleotides are synthesized progressively on the basis of phosphoribose molecules, not by first synthesizing purine bases alone and then combining them with phosphoribose. The remedial synthesis of purine nucleotides is mainly due to the lack of enzymatic systems for the ab initio synthesis of purine nucleotides in certain tissues and organs of the body, such as brain and bone marrow, so that only this pathway can be performed, and this pathway saves energy and some amino acid consumption during ab initio synthesis.