Products
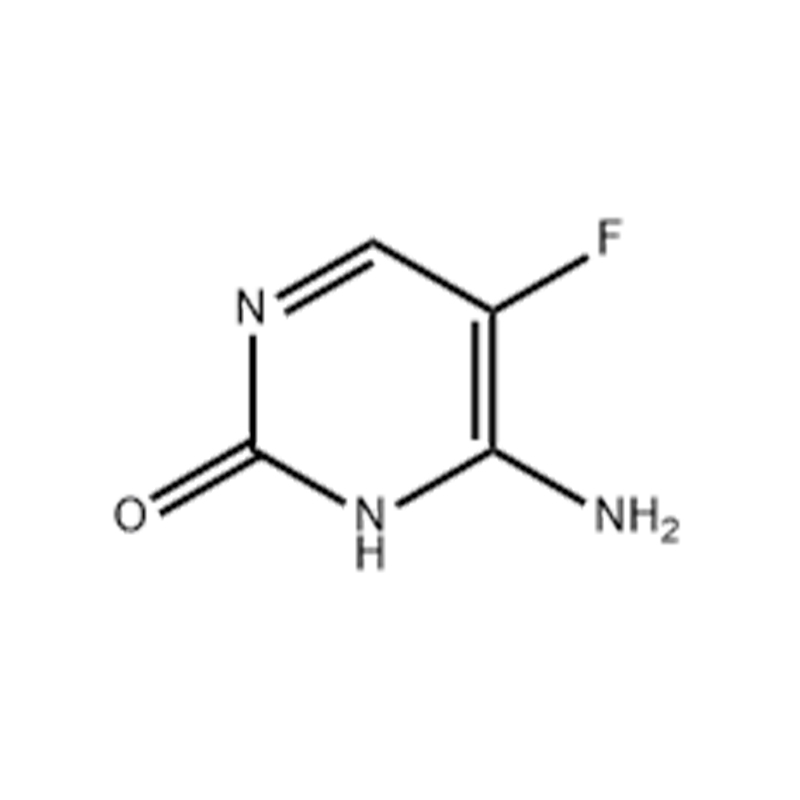
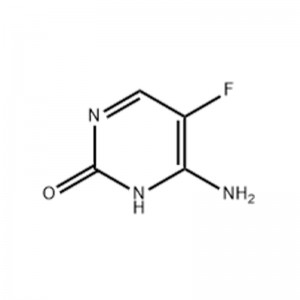
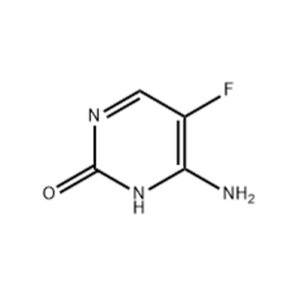
5-Fluorocytosine
Structural Formula
Physical
Appearance: White powder
Density: 1.3990 (estimate)
Melting point: 298-300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Boiling point.
Refractivity
Flash point.
Safety Data
Hazardous category.
Dangerous Goods Transport Number.
Packing category.
Application
Flucytosine by mouth is used for the treatment of serious infections caused by susceptible strains of Candida or Cryptococcus neoformans. It can also be used for the treatment of chromomycosis (chromoblastomycosis), if susceptible strains cause the infection. Flucytosine must not be used as a sole agent in life-threatening fungal infections due to relatively weak antifungal effects and fast development of resistance, but rather in combination with amphotericin B and/or azole antifungals such as fluconazole or itraconazole. Minor infections such as candidal cystitis may be treated with flucytosine alone. In some countries, treatment with slow intravenous infusions for no more than a week is also a therapeutic option, particular if the disease is life-threatening.
Serious fungal infections may occur in those who are immunocompromised. These people benefit from combination therapy including flucytosine, but the incidence of side-effects of a combination therapy, particular with amphotericin B, may be higher.
5-Fluorocytosine is used to treat fungal infections caused by Cryptococcus and Candida, such as fungal sepsis, endocarditis, meningitis, and antifungal agents for lung and urinary tract infections
Characteristic
This product has high antifungal activity against Candida spp. and Candida spp. and also has antibacterial activity against Bacillus spp. and Mycobacterium spp. The product is antibacterial at low concentration and fungicidal at high concentration. The mechanism of action is to block the synthesis of fungal nucleic acid. The fungus is easy to produce resistance to this product.
Precautions
Combined with amphotericin B, it has synergistic effect, but it may reduce the excretion of this product from the kidney and increase the blood concentration, which may cause toxic reactions in the kidney and blood system. Therefore, the peak blood concentration should be monitored and maintained at 50-75μg/ml, not exceeding 100μg/ml; the use of bone marrow inhibitors may increase the hematologic toxicity of this product.
This product can cause ① nausea, diarrhea, rash, etc.; ② liver damage, mostly elevated liver function indicators, but also hepatomegaly or even hepatic necrosis; ③ myelosuppression leukocyte and platelet reduction, occasionally can cause whole blood cytopenia. Fatal granulocytic leukocyte deficiency and remitting anemia have also been reported; ④ hallucinations, headache and vertigo have also been reported. Therefore, use with caution in patients with hepatic or renal impairment, blood disorders, and bone marrow suppression. The peripheral blood picture, liver and kidney function and urine routine should be checked regularly when using this product. It has teratogenic effect in animal testing, and should be used with caution in pregnant women.
Adverse reactions include elevated transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, gastrointestinal symptoms, leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal impairment, headache, decreased visual acuity, hallucinations, hearing loss, dyskinesia, decreased serum potassium, calcium and phosphorus values, and allergic reactions (e.g. rash).